Automated Systems Design: Streamline Efficiency & Innovation
11.16.2023
Automated systems design is revolutionizing the way businesses operate in our rapidly evolving landscape. Automation, in various forms, has permeated nearly every aspect of our daily lives and has become integral to modern businesses. It’s no longer a luxury, but a necessity. Automated systems, designed to streamline efficiency and foster innovation, have become essential tools for organizations seeking to remain competitive and thrive in a highly dynamic global marketplace.
Automated systems are essentially a set of software and hardware components that perform tasks with minimal human intervention. These systems have the potential to revolutionize industries, offering advantages that include increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, improved accuracy, and the ability to handle complex, repetitive tasks. Through automated systems design, businesses can optimize processes, minimize errors, and adapt swiftly to changing demands, ensuring they stay ahead in today’s fast-paced world.
Here, we will explore how automated systems design can drive efficiency and innovation across various sectors.
What is Automated Systems Design?
Automated systems design refers to the process of creating and implementing systems that can perform tasks and processes with minimal human intervention or oversight. These systems typically consist of a combination of software, hardware, and often sensors and control mechanisms. The primary goal of automated systems design is to streamline and optimize processes, reduce human error, improve efficiency, and enhance productivity in various industries and domains.
Key Elements of Automated Systems Design
1. System Identification
This phase of automated systems design involves a thorough system design analysis of existing processes to identify which tasks or workflows can benefit from automation. This requires understanding the current workflow, including inputs, outputs, and intermediate steps. It’s important to identify tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, error-prone, or require rapid response times, as these are prime candidates for automation systems and design. The goal of automation system design identification is to pinpoint the areas where automation can lead to efficiency gains and operational improvements.
2. Hardware and Software Integration
Hardware and software are the foundational components of an automation system design. Hardware may include robots, sensors, actuators, computers, and other physical devices necessary to perform tasks. Software is responsible for controlling and managing the hardware components, executing tasks, and making decisions. It includes algorithms, control logic, and software interfaces. The selection and integration of the right hardware and software components are critical to ensuring the system’s reliability and effectiveness.
3. Control and Decision-Making Algorithms
Control and decision-making algorithms form the “brain” of the automated systems design. These algorithms determine how the system responds to various inputs, conditions, and situations. Algorithms are designed to handle a wide range of scenarios in automated systems design, ensuring that the system can operate effectively and autonomously. They may incorporate if-then rules, machine learning models, or other decision-making processes. The design of these algorithms is influenced by the specific requirements and goals of the automated system, whether it’s for manufacturing, autonomous vehicles, or any other application.
4. Sensors and Data Acquisition
Sensors are used to collect data about the environment, the status of the system, and any relevant variables. They can include cameras, temperature sensors, motion detectors, and more, depending on the application. Data acquisition involves gathering, processing, and transmitting data to the control software. This data is essential for automated systems design so that the system can make informed decisions, adapt to changes, and operate effectively. Sensors play a crucial role in providing real-time information that enables the system to respond to its surroundings.
5. Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
The HMI is the means through which human operators interact with and monitor the automated system. It provides real-time information on the system’s status and performance. HMIs often include user-friendly graphical interfaces that display data, allow for manual control or intervention, and provide alerts or notifications. Building the HMI alongside a design system is crucial, as it ensures that human operators can oversee and manage the automated system, making it easier to intervene when necessary.
6. Safety Protocols
Safety is a paramount concern in automated systems design, especially in applications involving machinery or critical processes. Safety protocols are implemented to prevent accidents and mitigate risks. These protocols may include emergency stop mechanisms, safety sensors, protective barriers, and fail-safes that trigger specific actions when safety-critical conditions are detected. Ensuring the safety of the system, its operators, and the surrounding environment is an essential aspect of automated systems design.
7. Testing and Validation:
Before deploying an automated systems design, thorough testing and validation are necessary. This involves subjecting the system to a wide range of scenarios to ensure that it performs as intended. Testing verifies that the system’s hardware, software, and algorithms function correctly and efficiently. Validation confirms that the system meets safety standards and regulatory requirements. Rigorous UX testing and validation procedures help identify and rectify any issues or shortcomings in the automated systems design before it goes into operation.
8. Scalability and Flexibility
Automated systems design should be developed with scalability and flexibility in mind. They should be capable of adapting to changing requirements and expanding or contracting as needed. Scalability ensures that the system can handle increased workloads or new tasks without a complete redesign. Flexibility allows for adjustments to be made to accommodate evolving needs or conditions. This adaptability is crucial in dynamic environments where businesses need to respond to market changes or evolving technological capabilities.
Automated systems design involves a comprehensive process of identifying tasks suitable for automation, integrating hardware and software, implementing control and decision-making algorithms, leveraging sensors and data acquisition, providing human-machine interfaces, ensuring safety, conducting testing and validation, and designing for scalability and flexibility. These elements work together to create efficient, reliable, and innovative automated systems across various industries and applications.
Benefits of Automation Systems and Design
The benefits of automation systems and design are multifaceted and encompass various aspects of organizational operations. Here are some key advantages of automated system design:
Improved Efficiency
Automated systems streamline processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing errors. Tasks that would traditionally require significant time and resources can be completed quickly and accurately through automation systems and design, leading to improved overall efficiency.
Cost Savings
By automating repetitive tasks, organizations can reduce labor costs and free up resources to allocate towards more strategic initiatives. Additionally, automated systems design can lead to savings in terms of reduced errors, lower operational overheads, and optimized resource utilization.
Enhanced Productivity
Automated systems design enables employees to focus on high-value tasks that require creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. By offloading routine and repetitive tasks to automated systems, employees can work more efficiently and effectively, leading to increased productivity across the organization.
Faster Time-to-Market
Automated systems design expedite the development and deployment of products and services, allowing organizations to bring new offerings to market more quickly. By automating various stages of the production or development process, businesses can shorten time-to-market cycles and gain a competitive edge.
Improved Accuracy and Consistency
Automated systems design perform tasks with a high degree of accuracy and consistency, reducing the risk of human error. This ensures that processes are carried out reliably and according to predefined standards, leading to higher-quality outputs and better outcomes.
Scalability
Automated systems design are inherently scalable, allowing organizations to easily accommodate fluctuations in demand or scale operations as needed. Whether it’s processing a large volume of transactions or expanding into new markets, automation systems and design provide the flexibility to scale operations efficiently.
Data-driven Decision Making
Automation systems and design generate valuable data and insights that can inform decision-making processes. By capturing and analyzing data in real-time, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their operations, identify areas for improvement, and make more informed strategic decisions.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Automation enables organizations to deliver faster, more personalized, and consistent customer experiences. Whether it’s through automated customer support, personalized recommendations, or streamlined order processing, automation can help organizations meet and exceed customer expectations.
Overall, automation system design offers organizations a wide range of benefits, from improving efficiency and productivity to driving innovation and delivering superior customer experiences. By embracing automation, organizations can position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly competitive and dynamic business environment.
How Can Automated Systems Design be Implemented?
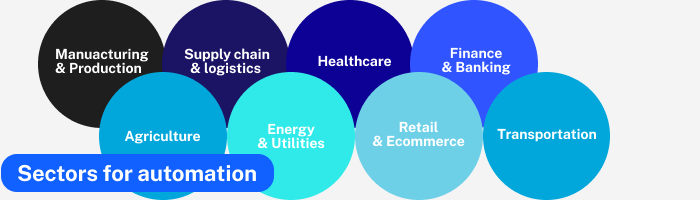
Automated systems design can be applied across various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, finance, agriculture, energy, and more. The specific design process and technologies used will vary depending on the application and the desired outcomes. Automated systems are a critical part of the broader field of automation system design, which aims to reduce manual labor, increase efficiency, and enable innovation in numerous sectors.
1. Manufacturing and Production
The manufacturing sector has been at the forefront of automation system design for many years. Automated systems design has revolutionized production processes, leading to higher precision, consistency, and speed. Industrial robots and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines have taken over tasks that were once manual, resulting in reduced errors and enhanced product quality.
Automation system design also plays a pivotal role in lean manufacturing, as it allows companies to adjust production rates in real time to meet fluctuating demand. Smart factories and the Internet of Things (IoT) enable machines to communicate with each other, optimizing production, predicting maintenance needs, and minimizing downtime.
2. Supply Chain and Logistics
Automated systems design has significantly transformed the supply chain and logistics sector. Warehouse automation system and design, which includes automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), autonomous forklifts, and conveyor systems, has greatly improved the speed and accuracy of order fulfillment. Automated tracking and tracing systems, coupled with data analytics, provide real-time visibility into the movement of goods, reducing the risk of delays and improving decision-making.
Autonomous vehicles and drones have also become key players in last-mile delivery, increasing efficiency and reducing delivery times. This shift toward automation system design in supply chain and logistics enables businesses to meet consumer demands faster and more reliably.
3. Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, automated systems design has led to improved patient care and increased operational efficiency. Electronic health records (EHR) systems have replaced paper-based records, allowing healthcare providers to access patient data instantly, make more informed decisions, and reduce errors.
Robotic surgery systems enable surgeons to perform intricate procedures with higher precision. Automated pharmacy systems ensure the accurate dispensing of medications, reducing the risk of medication errors. Telemedicine platforms are revolutionizing patient access to healthcare services, allowing consultations to take place remotely and expanding the reach of medical expertise.
4. Finance and Banking
The financial sector has seen a significant transformation through automated systems design. High-frequency trading algorithms can execute complex trading strategies within microseconds, allowing financial institutions to respond rapidly to market changes. Automated customer service chatbots have improved the efficiency of handling routine customer inquiries, while machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to detect fraudulent transactions.
Automation has also enhanced the accuracy and speed of loan origination, underwriting, and risk assessment in banking. This not only benefits the institutions but also streamlines the lending process for customers, making access to financial services more efficient and accessible.
5. Agriculture
Agriculture is another sector where automated systems are driving innovation. Precision agriculture utilizes automated drones, sensors, and autonomous tractors to monitor and manage crops, increasing yield and minimizing resource wastage. These technologies have the potential to address global food security challenges by optimizing farming practices.
Read: System Design: Safeguarding Your Space
Automated irrigation systems and monitoring tools help farmers conserve water and reduce operational costs. Furthermore, automated harvesting equipment speeds up the harvesting process, reducing labor requirements and ensuring timely crop collection.
6. Energy and Utilities
In the energy and utilities sector, automated systems design is revolutionizing the
management of power generation and distribution. Smart grids use automated sensors and analytics to optimize energy distribution, reduce losses, and improve the overall efficiency of the electrical infrastructure. Automated energy management systems in commercial and residential buildings enhance energy efficiency and sustainability.
The automation of power plants, whether conventional or renewable, allows for better control, monitoring, and predictive maintenance, which reduces downtime and improves overall reliability.
7. Retail and E-commerce
The retail industry has been reshaped by automated systems design, particularly in the context of e-commerce. Automated inventory management and order fulfillment systems in warehouses ensure that products are readily available for shipment. Recommendation engines use machine learning to suggest products to customers based on their preferences and browsing history, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
Self-checkout kiosks and contactless payment methods have streamlined the shopping experience, reducing wait times and enhancing the overall shopping experience. Additionally, automated chatbots and virtual shopping assistants provide customer support and information, improving customer engagement.
8. Transportation
The transportation industry is experiencing a significant transformation with the advent of
autonomous vehicles and smart transportation systems. Automated traffic management systems optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve safety. Autonomous vehicles, whether in the form of self-driving cars or autonomous buses, have the potential to reduce accidents and increase transportation efficiency.
sdseAutomated systems design also plays a critical role in the development of smart cities, where transportation, infrastructure, and utilities are interconnected and managed in real-time to enhance the quality of life for urban residents. Additionally, all of these automated systems are reliant on the consistent elements of a design system for human interfacing throughout the experience.

Automated systems design is a driving force behind efficiency and innovation in a wide range of industries. As businesses and organizations strive to remain competitive and meet the ever-increasing demands of the modern world, automation becomes an imperative. By embracing automated systems, companies can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and create an environment where innovation can flourish.
The future holds even more promise for automation, as it continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in terms of efficiency and innovation across various sectors.
Automated systems can’t exist without a comprehensive design system, luckily our design system development services are tailored to encapsulate every vital design aspect. From boosting efficiency and productivity to fostering innovation and ensuring user satisfaction, we specialize in creating systems that are not only adaptable and cost-effective but also user-centric, ensuring that they meet the evolving needs of your business and your customers.
By partnering with DOOR3, you’re not just investing in a system; you’re investing in a future-proof solution that aligns with your strategic goals, enhances your operational efficiency, and elevates your user experience to new heights. Let’s collaborate to build a system that not only solves today’s challenges but also paves the way for tomorrow’s opportunities. You can reach out to us by contacting us here.
FAQs: Automated Systems Design
How does automated systems design differ from traditional manual systems design?
Automated systems design differs from traditional manual systems design in fundamental ways, primarily revolving around the level of human involvement, efficiency, and scalability. In traditional manual systems design, tasks are predominantly carried out by human operators, relying on physical effort and time-consuming processes. Conversely, automated systems design aims to minimize human intervention by leveraging machinery, robotics, and computer systems to execute tasks autonomously and with precision.
This transition enables significant improvements in efficiency and speed, as automated processes can complete tasks at a much faster pace than their manual counterparts. Moreover, automated systems ensure greater accuracy and consistency in task execution, reducing the likelihood of errors or inconsistencies that may arise from human factors.
What role does software play in automation system design?
In automation system design, software plays a pivotal role as the central component that orchestrates and controls the operation of hardware devices and systems. Software programs define the logic, algorithms, and sequences of actions that govern how automated processes are executed, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and reliability.
What are some best practices for ensuring safety in automation system design?
Ensuring safety in automation system design involves implementing several best practices to mitigate risks and protect personnel, equipment, and the surrounding environment. Firstly, conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards and comply with relevant safety standards and regulations is essential. Implementing safety interlocks and emergency stop mechanisms, along with providing comprehensive safety training and clear procedures for routine operation and maintenance, are crucial steps.
What are the latest trends and advancements in automation system design?
The latest trends and advancements in automation system design are driven by emerging technologies and industry demands for increased efficiency, flexibility, and connectivity. One significant trend is the integration of Industry 4.0 principles and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, enabling seamless connectivity and data exchange between devices and systems.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms are increasingly being integrated into automation systems to enable autonomous decision-making, predictive analytics, and adaptive control.